The foundation is the most crucial investment in any construction work since it forms the basis on which all the other constructions rest. An effective foundation makes the building sturdy. It stops it from settling and shields it against moisture, changing soils, and long-term damage.
That is why you need to know how much a foundation costs before you hit the ground. By understanding the cost of footings and slab, you can avoid budget overruns and ensure smooth project planning.
On average, the foundation cost per square foot ranges between $6 and $15, based on the soil condition, materials, reinforcement, and workforce needs. This blog breaks down everything you should know about foundation costs, cost factors, and smart budgeting plans. so lets get into it.
Understanding foundation pricing starts with smart construction budgeting to avoid costly overruns.
Foundation Cost Estimator: Pricing by Square Footage
A foundation cost estimator is one of the easiest tools to use to understand your budget based on total square feet.
Many contractors and developers calculate the foundation cost per square foot using this method, as it provides a starting point when detailed drawings and soil reports are not available. Here is a breakdown of the estimated house foundation cost.
Estimated Foundation Cost By Home Size
| Home Size (Sq Ft) | Estimated Cost Range | Average Cost |
| 500 sq ft | $3,000 – $7,500 | ~$5,250 |
| 1,000 sq ft | $6,000 – $15,000 | ~$10,500 |
| 1,500 sq ft | $9,000 – $22,500 | ~$15,750 |
| 2,000 sq ft | $12,000 – $30,000 | ~$21,000 |
| 2,500 sq ft | $15,000 – $37,500 | ~$26,250 |
These estimates normally entail excavation, formwork, reinforcement, and the placement of concrete, but can vary according to labor rates, accessibility, and the preparation of the soil.
Foundation Cost for 1000 Sq Ft
For an easier comparison, let’s see the breakdown for the foundation cost for 1000 sq ft. This size is often taken as a standard, as it represents the cost structure of a typical residential project. It shows how the materials, labor, and preparation work are combined to create the overall investment.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost Range |
| Site Preparation & Excavation | $1,200 – $3,000 |
| Footings Construction | $1,500 – $3,500 |
| Concrete Slab Pouring | $2,000 – $4,500 |
| Reinforcement (Rebar & Mesh) | $800 – $2,000 |
| Labor & Equipment | $1,500 – $3,000 |
| Total Estimated Cost | $6,000 – $15,000 |
The example shows the distribution of the foundational costs to various phases of construction. Small homes may face higher per square foot costs due to fixed mobilization costs, whereas larger homes benefit from economies of scale, reducing the average cost per unit area.
Material Breakdown for Concrete, Cement, and Reinforcement Costs
Material selection is one of the biggest factors affecting the total foundation costs. The cement foundation cost comprises several elements that produce a stable structure:
- Concrete Mix: The concrete mix is normally priced at between 120 and 170 dollars per cubic yard, depending on the required strength.
- Gravel Base Layer: This gives it stability and drainage, and costs on average 10-20 per square foot to install.
- Reinforcement Steel (Rebar): Enhances the load-bearing capacity and crack resistance.
- Formwork and Vapor Barriers: Assist in shaping the slab and avoiding the damage of moisture.
- Stronger mixes or reinforcement could be needed in heavier buildings or problematic soil, resulting in increased building material costs.
Site conditions, soil type, and grading affect material quantities and foundation stability; learn more about proper preparation in our grading in construction guide.
A Comprehensive Comparison of Foundation Types
The foundation type influences the durability, construction time, and the entire budget of your project. Each of them has certain benefits based on the soil conditions, climate, and the purposes of the project. The following analysis will help you choose the right foundation type for your project.
Concrete Slab Foundation
It is the most popular foundation of residential projects. A concrete slab foundation is also cheap and easy to build, with just a single layer of concrete being poured on a pre-existing foundation. It works best on buildings that are built on stable surface soil and will not be expensive to pay for. The concrete slab foundation cost ranges between $5 and $14 per square foot.
Pros
- Lowest construction cost
- Rapid deployment (can be accomplished in days)
- Little maintenance is needed.
- Minimal chances of pest intrusion.
Cons
- Poor accessibility to amenities or plumbing.
- It is not a good fit in cold climates with freeze-thaw periods.
- The repair can be more invasive in case of problems.
Pier and Beam Foundation
Pier and beam systems raise the structure with the help of the vertical piers that are planted in the ground and the beams that are used to support the building load. This type of design is particularly convenient on hilly or not very stable ground. The Average pier and beam foundation cost is $8 – $15 per sq ft.
Pros
- Lifts the building above damp land.
- More convenient access to utilities.
- Grows in different soil conditions.
Cons
- Maintenance will be more expensive in the long run.
- Needs ventilation and insulation design.
- A bit above the price of slab foundations.
For a comparison with other foundation types and real-world pricing, see our article on 40×80 concrete slab cost
to understand how slabs differ from pier and beam designs.
Crawl Space Foundation Estate
A crawl space foundation would be appropriate in regions with high soil moisture. It lifts the home off-the-ground to a few inches or 3 feet high, protecting the structure against dampness and water destruction. The crawl space foundation is more expensive than a normal slab foundation because of the additional materials and labor spent. The crawl space foundation cost can vary from $10,000 and $36,000 per square foot.
Pros
- Access to Plumbing, wiring, and HVAC.
- Greater resistance to ground moisture than slabs.
- Better insulation alternatives.
Cons
- Should be well-ventilated to avoid mold.
- More expensive than slab foundations.
- Requires constant skin care.
Basement Foundation
A basement foundation is the most preferable type of foundation in case the project needs additional living or storage space. The basement foundation cost is higher than a slab and crawl space foundation cost because the excavation, concrete walls, drainage, and waterproofing are more expensive.
Pros
- Gives the building more square feet, but does not increase the size.
- Enhances property value and functionality.
- Well-built structural stability of multi-story constructions.
Cons
- Maximum construction and excavation costs.
- Needs a drainage system and waterproofing.
- Longer construction period.
A Quick Comparison of Foundation Types
| Foundation Type | Cost Range (Per Sq Ft) | Key Advantage | Main Limitation |
| Concrete Slab | $6 – $12 | Most affordable | Limited access to utilities |
| Pier and Beam | $8 – $15 | Great for uneven terrain | Higher maintenance |
| Crawl Space | $10 – $18 | Accessible and ventilated | Moisture control needed |
| Basement | $25 – $50 | Adds living/storage space | Most expensive |
Technical Considerations: Deep Foundations & Soil Quality
Not every structure can be based on shallow foundations or regular slabs. When the surface layer of soil is not strong enough to bear the weight of the structure, the engineers resort to deep foundation systems. It redistributes the weight of the structure to more stable soil or rock layers below.
How can Deep Foundations Help with Standard slab fails
A deep foundation is required when the upper soil layers are weak, expansive, or highly compressible. Instead of spreading the load across the surface like a slab-on-grade, deep foundations use elements such as piles, piers, or drilled shafts to anchor the structure into stronger subsurface strata. This approach prevents settlement, structural shifting, and long-term damage.
They increase the initial expenses by 20%, but deep foundations greatly decrease the chances of later structural failure and high costs in repair.
Deep foundations are applied where:
- The site of the building has low load-bearing capacity.
- High water tables cause surface instability.
- The building is massive or multi-story.
- Big soils undergo swellings and contractions repeatedly.
- The project will need additional resistance to lateral forces.
The Effect of Soil on Cost and Design: Clay vs. Sandy Soil
The type of soil is one of the most important factors that will determine the depth of the footing, the design of the foundation, and the ultimate price.
Clay Soil
Clay swells and contracts as it gets wet and dry, producing unending movement underneath the structure. This behavior requires:
- Deeper and wider footings
- Additional reinforcement
- Moisture control system
- Pier-founded foundations
- These extra requirements add to excavation, material, and workforce.
Sandy Soil
The sandy soil does not retain water, and it offers a more stable support. It is easy to work with it. The foundations in the sandy conditions usually demand:
- Shallower footings
- Less reinforcement
- Rapid excavation and installation.
Strategies for Cracks and Foundation Repairs
Foundation problems can arise over time due to soil movement, alterations in the moisture, or natural settlement. Thus, if you see a crack in a concrete slab foundation, you can use the following strategies to overcome it.
- Check whether you have visible cracks, uneven floors, or doors and windows with gaps in order to identify the first signs.
- Use epoxy or polyurethane injections to seal hairline cracks and prevent water infiltration.
- Make sure that you grade it correctly. Install gutters and channel water far away from the foundation to minimize the expansion and contraction of the soil.
- In regions that have weak or moving soil, soil compaction or underpinning may be used to maintain foundation stability.
- The addition of rebar, carbon fiber straps, or steel supports enhances the structure and prevents cracking of the structure in the future.
- Ensure that the soil around is kept moist to prevent shrinkage and expansion, which may cause the foundation to be stressed.
- Take professional help for large cracks to ascertain whether slab jacking, installation of piers, or complete repair of the structure is the solution.
Factors Influencing Foundation Costs
The overall concrete foundation cost is determined by several important factors, and their understanding can enable homeowners and builders make more accurate budgets. These factors are the type of foundation, the size and thickness of the foundation, the site conditions, the location, and the complexity of the project design.
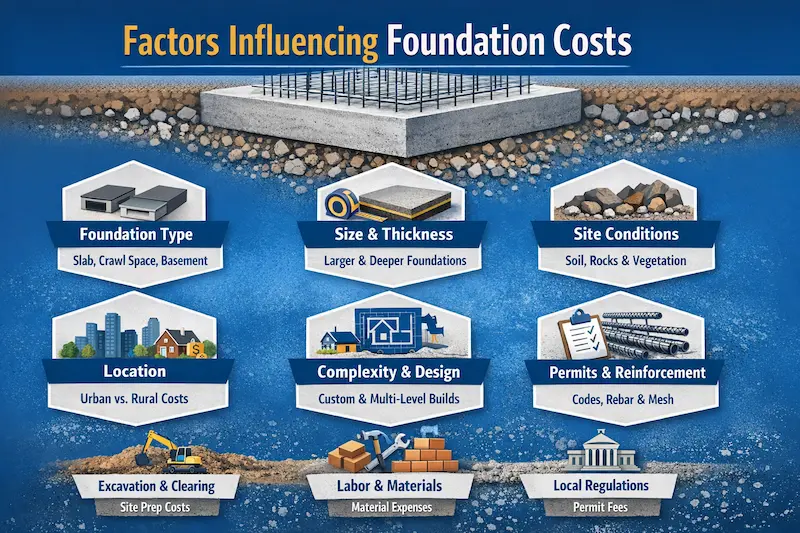
Foundation Type
The nature of the foundation used is a great determinant of the total cost involved. The type of foundation commonly used by the contractors depends on the size of the building, the soil, and the site preparations.
Size and Thickness of The Foundation
The total concrete foundation cost is proportional to the thickness and size of the foundation. The bigger the building, the more materials have to be used, whereas the smaller the building, the lower the cost and the smaller the foundation. The foundation height is also important, as commercial buildings usually demand stronger foundations. And in most residential projects, they do not demand more than 8 inches.
Site Condition
The site conditions have a direct impact on the cost of the foundation. Rocks, vegetation, or irregular ground areas will demand more excavation and pre-preparation, whereas poor soil can demand stabilization to carry the structure. These extra works add to the cost of a concrete slab foundation per square foot.
Location
The location of the project is a significant contributor to foundation pricing. Cities that are characterized by high material and labor rates will increase the cost of a concrete foundation. Whereas, the remote areas might be cheaper in material cost but more expensive when it comes to labor, equipment, and transportation costs.
Complexity and Project Design
The intricacy of the building design in terms of multiple corners and angles or the heavy bearing structure, upholds the requirement of a stronger foundation, as the cost of the basement foundation or crawl space foundation is higher. Much simpler designs are usually less costly to build since fewer materials and labor are needed.
Excavation and land clearing
The location should also be cleared and evened before construction by removing trees, rocks, and debris, and ensuring that the ground is cleared to form a stable base. The cost of excavation can be between 1,200 and 5,000 dollars on residential projects, depending on the difficulty of the soil and the equipment needed.
Local Building Codes and Permits.
Construction permits and inspections ensure that the foundation is in accordance with structural and safety standards. The cost of the permit is normally between 500 and 3000 dollars, and this varies with the size of the pending project and the demands of the municipality. Compliance-related costs in most areas are between 3 and 5 percent of the overall foundation budget, which involves approvals of engineering and inspection of the sites.
Costs of reinforcement (Rebar and Mesh)
The steel reinforcement is essential to enhance the durability and stop cracking under loading. Rebar installation typically costs between $0.80 to 1.50/ sq ft, and wire mesh another 0.30 to 0.60/ sq ft.
Estimating reinforcement costs, including rebar and mesh, can be simplified by reviewing our estimate construction costs guide for precise budgeting tips.
Stop guessing your project expenses and start planning with precision using our expert data.
Conclusion
The success of any construction project depends on a well-planned foundation. When choosing the type of foundation, knowing the Cost of footings and slab, material, and labor allocation offers long-term stability.
So if you want to plan smartly and lead a successful project, then a deep understanding of these cost breakdowns is a must. Cost Bidding estimates footing and slab prices for your construction project with accuracy.
FAQs
What is the price of the foundation per square foot?
The general cost of the foundation per square foot varies between 6 and 15 dollars, depending on the type of foundation, the soil quality, the reinforcements required, and the labor charge.
What is the most expensive kind of foundation?
A basement foundation is normally the most expensive as it involves deeper excavations, structural walls, drains, insulation, and waterproof sealing.
What affects the total cost of footings and slab?
Pricing is influenced by choices of materials like the thickness of the concrete layers, the rebar/mesh reinforcement, or the waterproofing. The nature and quality of the soil also dictate the depth and width of the footings to be used, and the position in which the structure is going to be built.
What requirements are required to finish a concrete foundation?
Concrete foundations usually require 1 to 2 weeks. The bigger or more complicated construction can be more time-consuming as it may entail further excavation, curing time, inspection, or weather delays in construction placement and finishing.
How much does the foundation of a 1,000 sq ft home cost?
The average cost of building a 1000 sq ft house would range between 6,000 and 15,000 dollars. This covers excavation, footings, laying of the concrete, reinforcement, and labour.




